Editor: an application to write or modify files that only contain
plain text, similar to a typewritten page. An editor doesn't support any
formatting (like different fonts, spacings etc.). It's main use is for simple
notes or for program files.
- Editors usually have a text area, where text can be written at the current
input position (the cursor, indicated by a special symbol). Using the
mouse one can position the cursor anywhere and insert or delete text at that
point. If the text doesn't fit into the text area, special slider
(scrollbars) appear, which allow to move the displayed area over the
text.

- Further editor commands can be reached via the menues or
alternatively via special key combinations (e.g. Control-X).

- A basic feature is to mark a part of the text by dragging with the mouse. The
following three funtions can be applied to marked text:
| Command |
Function |
| Cut |
delete the marked text and copy it into an internal buffer (clipboard) |
| Paste |
insert the content of the clipboard at the cursor position |
| Copy |
put the text into the clipboard without deleting it |

- Other important commands are
| Command |
Function |
| New |
create a new text file |
| Open |
load an existing text file for editing |
| Save |
save the new text into the file |
| Close |
leave the editor |
| Search |
find a special word or string |
| Replace |
replace one (or all) appearances of |
| |
a string by another one |
| Help |
explain the editor commands |
-
- Some editors have very sophisticated features, especially for supporting the
creation of program files.
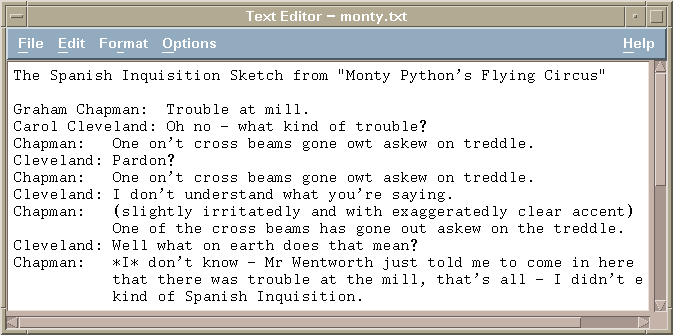
- The simple standard editor for Windows is called notepad:

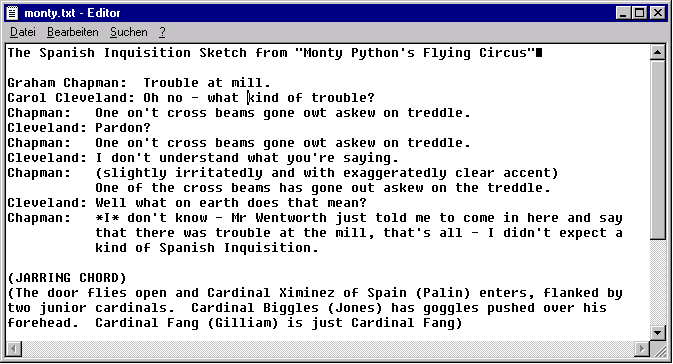
- For CDE the standard editor is called dtpad:

Peter Junglas 8.3.2000
![]()